Newsletter
You can sign up for our e-mail newsletter to be informed about the developments.


There are many known causes of skin aging, but “photoaging,” caused by sun damage, is the number one reason for premature aging. Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, which is our planet’s most important source of heat and light, are the primary enemy of skin cells. Sunlight can cause serious damage to skin cells, particularly to their DNA.
If the damage caused by sunlight to the DNA structure of the epidermis and dermis layers is not fully repaired, the structure of these layers can deteriorate over time. Additionally, the chemical substances released during the burning process are known to damage the dermis layer, particularly affecting the collagen and elastin fibers that prevent skin wrinkling. Skin that has been directly damaged by UV rays and is unable to produce elastin becomes dry and stiff. In hardened skin, capillaries and wrinkles begin to appear. In some people, the epidermis thins and becomes more sensitive. Additionally, the cells responsible for tanning eventually become nonfunctional, leading to the formation of brown spots on your skin. In more advanced cases, the skin turns yellow over time.
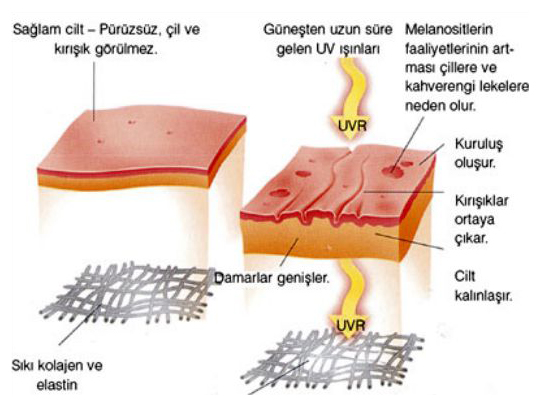
Uncontrolled, prolonged, intense, and unprotected sun exposure is the most effective skin aging factor, but the damage caused by sunlight to the skin goes beyond just aging. If these damages are not noticed, they can lead to lesions known as solar keratosis and even skin cancer.
It’s important to remember that sun damage does not occur overnight. Repeated exposure to UVA rays can deeply penetrate the skin, leading to collagen breakdown and preventing the production of healthy elastin in the tissue.
The easiest and simplest solution to protect yourself from the sun’s premature aging effects is to use sunscreen products regularly, regardless of the weather conditions or season. Until recently, it was thought that sunscreens with SPF 30 were sufficient to protect against the harmful effects of the sun. However, research has shown that in order to protect our skin from such negative effects, it is necessary to use products with SPF 50 and above that are “effective against photoaging”. Protecting yourself from sunlight, avoiding sun exposure during risky hours, using protective clothing and accessories (such as sunglasses, hats, and sun umbrellas), and applying high SPF products to visible parts of your skin during daylight hours are integral parts of the fight against sun-related issues.